Introduction
Blockchain technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency. Forget everything you think you know about blockchain technology. While it’s true that blockchain gained initial fame for supporting cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its potential applications reach far beyond the realm of digital money. This blog post dives into the exciting world of leveraging blockchain technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency. We’ll explore how this revolutionary technology is poised to transform numerous industries, from healthcare and finance to supply chain management and voting systems. So, buckle up and get ready to discover the future of blockchain.
Table of Contents
What is Blockchain Technology and How Does It Work?
Blockchain technology, often associated with cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, has the potential to revolutionize many aspects of our lives beyond the realm of digital currencies. What is blockchain exactly, and how does it work?
In essence, Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency is a secure and transparent way to record data. Imagine a public ledger that is constantly growing, where every transaction is meticulously documented and verifiable by anyone. This ledger isn’t a physical book, though. It’s a digital database distributed across a network of computers, making it tamper-proof and highly reliable.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components that make blockchain technology work:
1. Blocks: Think of digital Lego bricks. Each block stores information about a transaction, such as the date, time, and participants involved. This data can vary depending on the application of blockchain technology, which is explored in depth in the context of ‘Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency.
2. Chains: These blocks are chronologically linked and cryptographically secured, forming a chain. Each block contains a unique code and a reference to the code of the previous block, making it nearly impossible to alter any data within the chain without detection.
3. Hashing: Cryptography plays a vital role in securing blockchain data. A mathematical function called hashing is used to create a unique fingerprint (hash) for each block. Imagine a complex code generated from the block’s data. If any information within the block is changed, the hash will also change, alerting everyone on the network to a potential tampering attempt. Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency ensures the integrity and security of transactions across various applications.
4. Distributed Ledger: Unlike traditional databases controlled by a single entity, a blockchain is a distributed ledger. Copies of the entire blockchain are stored on multiple computers across the network. This decentralization ensures security and transparency. If someone tried to alter the ledger on one computer, the discrepancy would be identified by the other computers on the network.
Why is Blockchain Technology Useful Beyond Cryptocurrency?
While cryptocurrency brought blockchain technology to the forefront, its potential extends far beyond digital currencies. Here’s why blockchain technology is valuable in various industries:
1. Decentralization and Trust: Blockchain technology eliminates the need for a central authority to control and verify transactions. This decentralization fosters trust and transparency. No single entity can manipulate the data, and everyone on the network has access to the same immutable record. This is a stark contrast to traditional systems where a central body controls the data, potentially creating a single point of failure or manipulation.
2. Enhanced Security: Cryptography plays a crucial role in securing blockchain data. The use of hashing functions and a chained structure makes tampering with information highly difficult. Any attempt to alter a block would require altering all subsequent blocks as well, which would be nearly impossible on a large, distributed network.
3. Improved Transparency: All participants on a blockchain network can access the shared ledger, fostering transparency. Every transaction is recorded chronologically and immutably, providing a clear audit trail. This transparency can be crucial in areas like supply chain management or voting systems, where trust and auditability are paramount.
4. Increased Efficiency: Blockchain technology can streamline processes by automating tasks and eliminating intermediaries. Smart contracts, self-executing contracts stored on the blockchain, can automate agreements based on predefined conditions. This eliminates the need for manual verification and reduces the risk of errors, leading to increased efficiency.
5. Traceability: Since transactions are recorded chronologically on the blockchain, they can be easily tracked throughout the network. This traceability is valuable in applications like supply chain management, where it allows for tracking the origin and movement of goods.
In essence, blockchain technology offers a secure, transparent, and efficient way to record and manage data. These features make it a valuable tool for various industries beyond cryptocurrency, with the potential to revolutionize how we conduct business, manage information, and interact with each other.
What is the difference between Public and Private Blockchains?
Blockchain technology offers a versatile platform for recording and managing data. However, there are different types of blockchains designed to cater to specific needs. Here, we’ll explore the key differences between public and private blockchains in the context of Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency.
1. Public Blockchains:
Imagine a giant public ledger accessible to anyone. That’s essentially how Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency operates. Anyone can participate in the network, read and write transactions, and verify data. This openness fosters transparency and trust, making public blockchains ideal for applications where these aspects are crucial. Bitcoin and Ethereum are popular examples of public blockchains used for cryptocurrencies.
Here are several defining features of public blockchains:
- Open Participation: Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency Public blockchains operate like open communities. Anyone can join the network, participate in verifying transactions, and contribute to the overall security.
- Transparency: Every transaction on a public blockchain is visible to the public. This openness fosters trust by ensuring everyone can see what’s happening on the network.
- Decentralization: Public blockchains don’t have a central authority controlling the network. Instead, the power is distributed among participants, making it tamper-proof and resistant to manipulation.
- Security: Cryptography plays a vital role in securing public blockchains. Transactions are encrypted, and the chained structure makes altering data extremely difficult. Additionally, the distributed nature of the network strengthens security.
2. Private Blockchains:
Think of a private club with restricted access. Private blockchains operate in a similar fashion. A central authority controls access to the network, granting permission to specific participants. This controlled environment offers advantages in terms of scalability and efficiency, making private blockchains suitable for use cases where permission access and control are desired.
Here are some essential features of private blockchains:
- Permissioned Access: Unlike public blockchains, private blockchains function like exclusive clubs. Only authorized participants can join the network, granting control over who can access and contribute data. Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency
- Limited Transparency: Transactions on private blockchains may not be fully transparent. Access to details might be restricted to authorized participants, depending on the specific network configuration.
- Centralized Control: A single entity or consortium governs a private blockchain network. This centralized control streamlines decision-making but reduces the level of decentralization compared to public blockchains.
- Scalability: Private blockchains, such as those discussed in Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency, can potentially process transactions faster than public blockchains. The controlled environment with limited participants allows for faster verification and transaction processing.
Applications of Blockchain Technology Beyond Cryptocurrency
While cryptocurrency brought blockchain technology into the spotlight, its potential extends far beyond digital currencies. This innovative technology offers a secure, transparent, and efficient way to record and manage data, making it applicable to a wide range of industries. Here are some thrilling applications of blockchain technology that extend beyond cryptocurrency:
Supply Chain Management:
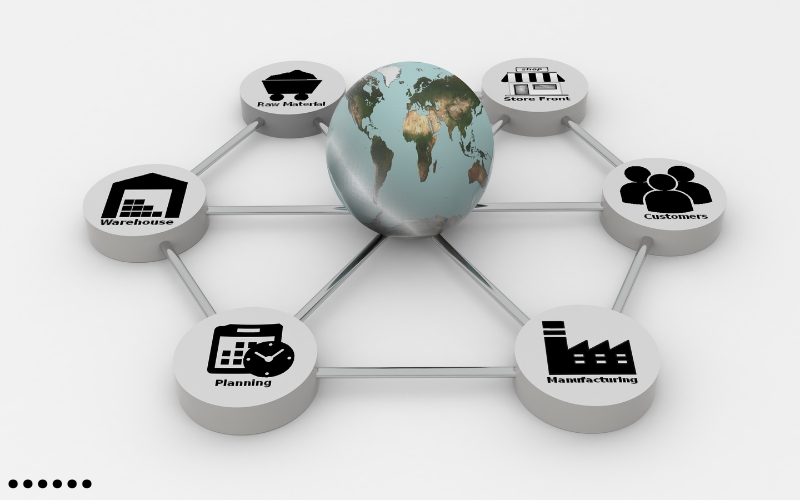
Imagine a complex web of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers working together to utilize blockchain technology to get a product from its origin to your doorstep. Traditional supply chains can be opaque, inefficient, and vulnerable to fraud. This is where Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency offers a revolutionary solution.
Challenges of Traditional Supply Chain Management:
- Lack of Transparency: Tracking the movement of goods through a complex supply chain can be challenging. It’s often difficult to pinpoint the origin and current location of products.
- Fraudulent Activities: Counterfeiting and product tampering are significant concerns in many industries.
- Inefficiency: Paper-based records and manual processes can slow down supply chains and increase costs.
- Limited Visibility: Stakeholders often lack real-time visibility into inventory levels and potential delays.
How Blockchain Technology Can Transform Supply Chains:
Blockchain technology provides a secure, transparent, and efficient method for managing supply chains. Here’s how:
- Immutable Record-Keeping: Every step in the supply chain journey, from raw materials to finished goods, can be recorded immutably on the blockchain. This creates a transparent and tamper-proof record that all authorized participants can access. Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency
- Enhanced Traceability: By tracking goods on the blockchain, companies can pinpoint the exact location and origin of products at any given time. This improves traceability and allows for faster identification of counterfeit products.
- Streamlined Processes: Smart contracts, or self-executing contracts on the blockchain, can automate tasks like payments and approvals, streamlining workflows and reducing manual processing.
- Improved Visibility: Real-time data on inventory levels, location, and potential delays can be readily available to all authorized participants, enabling better planning and decision-making.
- Increased Security: The cryptographic nature of blockchain technology makes it highly secure. Data tampering is nearly impossible due to the distributed ledger system.
Benefits of Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chains:
- Increased Trust and Transparency: All stakeholders can trust the information on the blockchain, fostering greater collaboration and trust throughout the supply chain.
- Reduced Fraud: The immutability of the blockchain record makes it difficult to alter data, mitigating counterfeit products and fraudulent activities.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined workflows and automated processes can lead to significant efficiency gains and cost reductions.
- Improved Inventory Management: Real-time visibility into inventory levels allows for better planning and reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
- Faster Dispute Resolution: With a clear and auditable record of transactions, disputes can be resolved more quickly and efficiently.
The Prospective Role of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management:
Blockchain technology is still evolving, but its potential to revolutionize supply chains is undeniable. As the technology matures and adoption grows, we can expect even greater benefits and innovative applications to emerge. In the next section, we’ll explore some real-world examples of how companies are leveraging Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency to transform their supply chains.
Secure Voting Systems:

Voting is a fundamental aspect of democratic societies, and ensuring the integrity of the voting process is crucial. Traditional voting systems, whether paper-based or electronic, have faced numerous challenges, including:
- Fraud and Tampering: Manipulation of votes and tampering with voting machines can undermine the election results.
- Voter Privacy: Ensuring the anonymity of voters while maintaining the integrity of their votes can be challenging.
- Accessibility: Making voting accessible to all eligible voters, including those with disabilities, is essential for fair elections.
How Blockchain Improves Voting Systems
Blockchain technology offers a robust solution to many of the challenges faced by traditional voting systems. Here’s how:
- Tamper-Proof Ledger: Every vote recorded on a blockchain is immutable, using Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures that the votes remain tamper-proof and accurately reflect the voters’ intentions.
- Transparency: Blockchain provides a transparent ledger that can be audited by all participants, ensuring that the voting process is fair and transparent. Voters can verify that their votes were counted without compromising their anonymity. Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency.
- Decentralization: Blockchain technology decentralizes the voting process, removing the necessity for a central authority and thereby diminishing the chances of manipulation and single points of failure.
- Security: Blockchain employs strong cryptographic algorithms to secure votes. Each vote is encrypted and linked to the previous one, making it nearly impossible for hackers to alter the results.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Blockchain-based voting systems can be designed to be accessible to all voters, including those with disabilities. Additionally, remote voting can be facilitated, allowing people to vote securely from any location.
Data Security and Privacy

Data security and data privacy are two intertwined concepts that are crucial in today’s digital world. Security, ensuring protection against unauthorized access and breaches, and immutability, maintaining data integrity, and preventing unauthorized changes are essential for safeguarding sensitive information.
Data security focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It’s about safeguarding the information itself and employing methods and technologies to ensure its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Data privacy deals with the control and ownership of personal information. It’s about giving individuals the right to decide how their data is collected, used, shared, and disposed of. This includes aspects like transparency (informing users about data practices), consent (obtaining user permission for data collection), and user access and control (allowing users to access and modify their data).
Analogy: Imagine your data as a valuable asset, like your house. Data security would be like the locks and alarm system on your house, protecting it from intruders. Data privacy would be like deciding who has keys to your house and setting rules about when they can visit.
Why are data security and privacy important?
Data breaches and privacy violations can have serious consequences, both for individuals and organizations. Here’s why they matter:
- Individuals: Identity theft, financial loss, reputational damage, and even physical harm can result from compromised data.
- Organizations: Data breaches can lead to hefty fines, loss of customer trust, and operational disruptions.
How to Ensure Data Security and Privacy
Below are several measures that individuals and organizations can implement:
- Individuals:
- Exercise caution when disclosing information on the internet.
- Use strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication.
- Exercise caution when clicking on links or opening attachments sent by unfamiliar senders.
- Ensure your software remains current by installing the newest security updates.
- Evaluate and modify privacy configurations for social media and other digital accounts.
- Organizations:
- Implement strong data security measures like encryption and access controls.
- Have clear data privacy policies that comply with regulations.
- Ensure clarity regarding the procedures for collecting and utilizing data.
- Provide users with control over their data.
Financial Services:
Financial services are the backbone of a healthy economy, providing a wide range of products and tools to manage your money. Whether you’re saving for a house, planning for retirement, or simply needing a safe place to keep your cash, financial services play a vital role.
What are financial services?
Financial services encompass a broad spectrum of economic activities that deal with the management of money. Here are some key areas:
- Banking: This includes traditional services like checking and savings accounts, money transfers, and loans. Banks also offer wealth management services for high-net-worth individuals.
- Investment: Financial advisors and brokerage firms help individuals and businesses invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other assets.
- Insurance: Insurance companies provide protection against financial losses due to unexpected events like accidents, illnesses, or property damage.
- Payments: Payment processors facilitate electronic transactions between buyers and sellers, ensuring secure and convenient money transfers.
Benefits of Using Financial Services
Financial services offer numerous advantages for individuals and businesses.
- Security: Banks and credit unions offer FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) or NCUA (National Credit Union Administration) insurance, protecting your deposits in case of an institution failure.
- Growth: Investment services allow you to grow your wealth over time potentially.
- Protection: Insurance safeguards you from financial burdens resulting from unforeseen circumstances.
- Convenience: Financial services make managing your money easier and more efficient, with online banking, mobile payments, and automated investment options.
Choosing the Right Financial Services
With a vast array of financial products available, it’s crucial to select the ones that suit your specific needs and goals. Here are some tips:
- Do your research. Understand the different types of financial services and compare offerings from various providers.
- Think about your objectives: Are you setting funds aside for an immediate need or planning for a future milestone, such as retirement?
- Assess your risk tolerance: How comfortable are you with potential investment losses?
- Seek professional advice. Financial advisors can help you create a personalized financial plan. pen_spark
Additional Applications:
The potential uses of blockchain extend beyond the topics listed above. Here are a few examples:
- Healthcare: Blockchain can revolutionize healthcare by providing a secure platform for managing medical records, facilitating secure data sharing, and streamlining insurance claims.
- Digital Identity Verification: Individuals could have more control over their digital identities with blockchain-based systems, allowing the secure sharing of verified information with authorized entities.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts stored on the blockchain automate agreements based on predefined conditions, streamlining processes across various industries.
- Real Estate: Blockchain can improve efficiency and transparency in real estate transactions by streamlining record-keeping and facilitating secure property ownership management.
- Public Sector: Governments can leverage blockchain for secure record-keeping, voting systems, and identity management, potentially enhancing transparency and efficiency.
- Energy Sector: Tracking energy consumption and facilitating secure peer-to-peer energy trading are potential applications of blockchain in the energy sector.
- Education: Blockchain can provide a secure platform for storing educational credentials and certificates, ensuring authenticity, and facilitating verification.
- Entertainment and Media: Combating piracy and ensuring fair artist compensation are areas where blockchain technology can potentially disrupt the entertainment and media landscape.
- The Internet of Things (IoT): Securing communication and data exchange between connected devices on the Internet of Things (IoT) is a potential application of blockchain technology.
- Environmental Sustainability: Blockchain can be used to track and verify sustainable practices in supply chains, promoting eco-friendly production and consumption.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: The immutable and auditable nature of blockchain data can simplify legal and regulatory compliance by providing a verifiable record of transactions and activities.
Conclusion: Blockchain Technology: Beyond Cryptocurrency
The future of blockchain technology is brimming with possibilities. While challenges remain in terms of scalability, sustainability, and privacy, ongoing advancements are paving the way for wider adoption across various industries. As blockchain continues to evolve, we can expect to see a more decentralized future where trust, transparency, and security are paramount.
Whether you’re a business leader, developer, or simply curious about the future of technology, it’s essential to stay informed about the data security and privacy implications of blockchain technology. This revolutionary technology, with its potential reaching far beyond cryptocurrency, has the power to transform the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. Are you ready to embrace the future of blockchain technology—beyond cryptocurrency?
FAQs
1. What exactly is blockchain technology?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers in a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof way. Imagine a giant, shared spreadsheet that everyone can access but no one can modify.
2. Isn’t blockchain just for cryptocurrency?
While cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin brought blockchain to the forefront, its applications extend far beyond finance. Blockchain can be used for secure data storage, supply chain management, voting systems, identity management, and much more.
3. How does blockchain-based technology ensure security?
The decentralized nature of blockchain is a key factor in its security. The data is encrypted and spread across multiple computers, making it very difficult to hack or tamper with.
4. What are the challenges facing blockchain technology?
Scalability, sustainability, and privacy are some of the key challenges that blockchain needs to address for wider adoption. New protocols and advancements are constantly being developed to overcome these hurdles.
5. How can I learn more about blockchain technology?
There are numerous online resources, courses, and communities dedicated to blockchain education. Stay tuned for future blog posts where we’ll delve deeper into specific applications of blockchain technology.




