Introduction
Encountering the “crawled not indexed” issue can be a major obstacle for any website owner striving for online visibility. When search engine bots crawl your pages but fail to index them, it can significantly impact your site’s presence in search results. In this blog post, we will explore the causes of this issue, how to diagnose it, and the best practices to ensure your pages are indexed and visible to your target audience. By following these steps, you can overcome the “crawled not indexed” problem and improve your website’s SEO performance.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Crawling and Indexing Process
To effectively address the “crawled not indexed” issue, it’s crucial to understand how search engines like Google operate. The processes of crawling and indexing are fundamental to this operation. Here is a simple explanation of these concepts:
Crawling
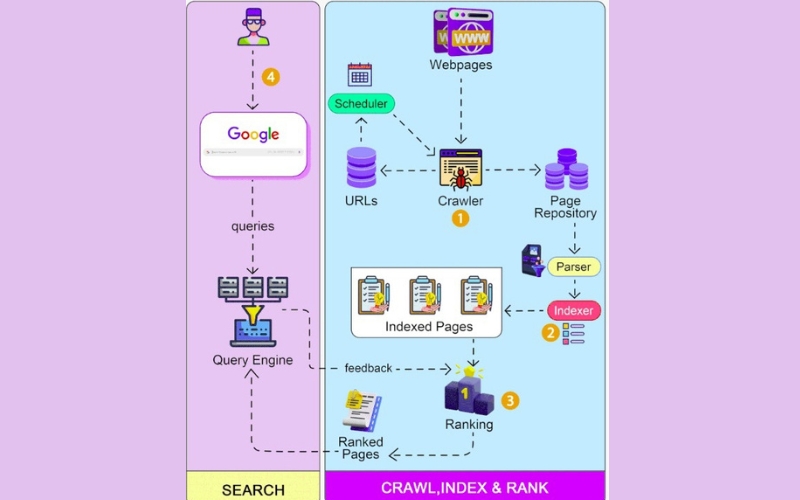
Crawling refers to the method search engines use to find and index fresh or updated content on the internet. Google uses automated programs called spiders or bots to scour the internet for new content. These bots start by fetching a few web pages and then following the links on those pages to find new URLs. This continuous process helps search engines keep their indexes up-to-date.

Indexing
Once a page is crawled, the search engine processes its content and stores it in an index, which is a massive database of discovered URLs. Indexing involves analyzing the content, the quality of the content, the relevance of the content, and even the freshness of the content. When a user enters a query, the search engine pulls relevant results from this index.
How Crawling and Indexing Work Together
Crawling and indexing work in tandem to ensure that when a user searches for something, they get the most relevant and timely information available. However, it’s important to note that not all crawled pages are indexed. This is where the “crawled not indexed” issue comes into play. If a page is crawled but not indexed, it means the search engine has found the page but has decided not to include it in its index.
Importance of Crawling and Indexing
For your content to appear in search engine results, it must first be crawled and then indexed. If your page is crawled but not indexed, it will not appear in search results, which can significantly impact your website’s visibility and traffic. Understanding these processes is essential for diagnosing and fixing issues related to the “crawled, not indexed” status.
Common Causes of the “Crawled Not Indexed” Issue
When dealing with the “crawled not indexed” issue, identifying the root cause is essential. Several factors can prevent your pages from being indexed by search engines, even if they have been crawled. Let’s explore some of the most common causes.
Technical Errors
Technical issues are one of the primary reasons for the “crawled not indexed” problem. These errors can prevent search engines from properly accessing or understanding your content.
- Server Errors (5xx Status Codes): If your server is down or experiencing issues when the search engine tries to crawl your site, it may result in server errors.
- Robots.txt File Blocking: A misconfigured robots.txt file can block search engines from crawling and indexing your pages.
- Incorrect Use of Noindex Tags: Using noindex tags on pages you want to be indexed will prevent them from appearing in search results.
Content Issues
Content quality and uniqueness play a significant role in whether a page gets indexed. Search engines aim to provide valuable and relevant content to users, and pages that fall short may not be indexed.
- Duplicate Content: Pages with content duplicated from other sites or within your own site can be de-prioritized by search engines.
- Thin Content: Pages with very little content or content that doesn’t provide substantial value to users may not be indexed.
- Low-Quality Content: Content that is poorly written, outdated, or not useful to users can also be a reason for non-indexing.
Website Structure
The way your website is structured can affect how search engines crawl and index your pages. Poor structure can lead to pages being crawled but not indexed.
- Poor internal linking: If your internal linking is weak, search engines may have difficulty discovering all your pages.
- Deep Pages Not Easily Accessible: Pages that are buried deep within your site’s structure, requiring many clicks to reach, might be missed during indexing.
Manual Actions
Manual actions from Google can also lead to your pages being crawled but not indexed. These actions are typically taken when a website violates Google’s guidelines.
- Google Penalties: If your site has been penalized for violating Google’s webmaster guidelines, affected pages may not be indexed.
- User-Generated Spam: Excessive spam content created by users on your site can lead to indexing issues.
Diagnosing the Problem
Identifying the root cause of the “crawled not indexed” issue is crucial for implementing the right solutions. Here are several methods to diagnose why your pages are not being indexed, despite being crawled.
Using the Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) is an invaluable tool for diagnosing the “crawled not indexed” problem. It provides detailed insights into how Google interacts with your website.
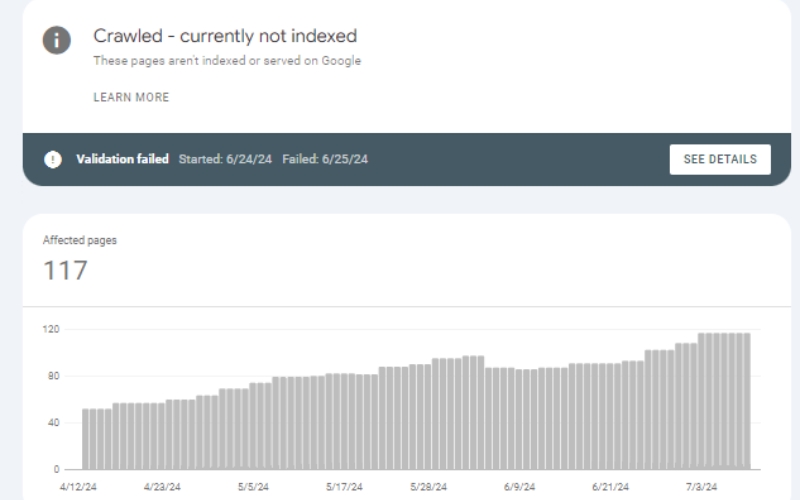
- Coverage Report: The Coverage Report in GSC shows the indexing status of your pages. Look for the “Crawled—currently not indexed” status to identify affected pages. This report also highlights errors and warnings that could be causing indexing issues.
- URL Inspection Tool: The URL Inspection Tool allows you to check the status of individual URLs. By entering a specific URL, you can see if it has been crawled and if any issues are preventing it from being indexed.
Analyzing Server Logs
Server logs provide a detailed record of how search engine bots interact with your site. By analyzing these logs, you can identify any issues that might be preventing indexing.
- Crawl Errors: Look for errors such as 5xx server errors or blocked resources that might be hindering indexing.
- Bot Activity: Check the frequency and patterns of bot visits to your site. If bots are not frequently visiting certain pages, those pages might not be indexed.
Checking Robots.txt and Meta Tags
Misconfigured robots.txt files and meta tags are common culprits for the “crawled not indexed” issue.
- Robots.txt File: Ensure your robots.txt file is not blocking search engines from accessing important pages. Use the Robots.txt Tester in GSC to verify your file’s configuration.
- Meta Tags: Check your pages for noindex meta tags. Accidentally using noindex tags on important pages can prevent them from being indexed.
Reviewing Page Quality and Content
Low-quality content can also lead to indexing issues. Evaluate your pages to ensure they meet Google’s quality guidelines.
- Duplicate Content: Use tools like Copyscape to check for duplicate content. Make sure each page provides distinct and valuable content.
- Content Depth: Assess whether your content is comprehensive and provides real value to users. Thin content is often overlooked by search engines.
Monitoring manual actions
Manual actions taken by Google can directly affect indexing. Check the Google Search Console for any notifications about manual actions against your site.
- Manual Action Report: This report details any actions taken by Google against your site, such as penalties for violating webmaster guidelines.
Ways to Resolve the “Crawled But Not Indexed” Problem
Once you’ve diagnosed the causes of the “crawled not indexed” issue, implementing effective solutions is the next crucial step. Here are some strategies to help ensure your pages get indexed by search engines:

Technical Fixes
Addressing technical issues is often the first step in resolving the “crawled not indexed” problem.
- Resolve Server Errors: Check for and fix any server errors (5xx status codes) that may be preventing indexing. Ensure your server is reliable and can handle search engine bots efficiently.
- Correct Robots.txt and Meta Tag Issues: Review your robots.txt file to ensure it’s not blocking important pages. Similarly, check your meta tags to ensure you’re not accidentally using noindex tags on pages you want indexed.
Content Optimization
Improving the quality and uniqueness of your content can significantly enhance your chances of getting indexed.
- Remove or Improve Duplicate Content: Identify and eliminate duplicate content. If removing is not an option, use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of the content to search engines.
- Enhance Thin Content: Add more valuable information to pages with thin content. Aim for comprehensive, well-researched, and engaging content that provides real value to users.
Request Re-indexing
If you’ve made significant updates to your pages or fixed issues that might have prevented indexing, requesting re-indexing can help expedite the process.
- Google Search Console: Use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to request indexing for specific URLs. This can be particularly useful after resolving technical issues or making substantial content updates.
- Re-submit Sitemap: If multiple pages need re-indexing, consider re-submitting your sitemap through Google Search Console to prompt search engines to crawl and index the updated pages.
Improving Website Structure
A properly structured website enables search engines to efficiently crawl and index your pages.
- Strengthen Internal Linking: Ensure your website has a strong internal linking structure. Links should help search engines discover all your pages easily. Think about generating a sitemap and submitting it to Google for indexing.
- Ensure Important Pages Are Accessible: Avoid burying important pages deep within your site. These pages should be accessible within a few clicks from the homepage.
Addressing manual actions
If manual actions are the cause of your “crawled not indexed” issue, following Google’s guidelines to rectify these actions is essential.
- Follow Google’s Guidelines: Carefully review the reasons for any manual actions against your site. Follow Google’s recommendations to fix the issues and request a review once the issues are resolved.
- Clean Up User-Generated Spam: If your site has user-generated content, ensure it is moderated to prevent spam and low-quality content from affecting your indexing status.
Best Practices for Ensuring Indexing
Ensuring your pages are indexed by search engines is crucial for visibility and driving traffic. Here are key best practices to prevent the “crawled, not indexed” issue.
Regularly update and add quality content.
Keep your website fresh with regular updates and high-quality content to signal relevance to search engines.
Submit a sitemap to Google.
Create and submit an XML sitemap through the Google Search Console to help search engines discover your pages.
Use structured data.
Implement schema markup to provide additional context about your content, aiding search engines in understanding your pages.
Optimize your website for mobile
Ensure your site uses responsive design and passes Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test for better indexing.
Improve site speed
Optimize site speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights. Pages that load quickly have a higher chance of being indexed.
Enhance internal linking
Create a strong internal linking structure to help search engines discover and index all your pages.
Monitor the Google Search Console
Regularly check the Google Search Console to stay informed about your site’s indexing status and resolve any issues.
Conclusion
Dealing with the “crawled, not indexed” issue can be frustrating, but understanding and addressing the root causes can significantly improve your website’s visibility in search results. By diagnosing the problem using tools like Google Search Console, addressing technical and content-related issues, and following best practices for indexing, you can help ensure your pages are properly indexed and reach your target audience.
Regularly update and enhance your content, maintain a well-structured website, and stay vigilant by monitoring indexing status through the Google Search Console. Implementing these strategies will not only resolve current indexing issues but also prevent future ones, ensuring your website remains competitive and visible in search engine results.
Remember, the goal is to create a user-friendly, high-quality website that search engines recognize and index. With consistent effort and attention to detail, you can overcome the “crawled, not indexed” issue and achieve better SEO performance.
FAQs
1. What does “crawled, not indexed” mean?
“Crawled, not indexed” means that search engine bots have visited your page but have not added it to the search engine’s index. As a result, the page will not appear in search results.
2. How can I check if my page is “crawled, not indexed”?
Use the Google Search Console to check the status of your pages. The coverage report will show if any pages are crawled but not indexed. You can also use the URL inspection tool for specific URLs.
Where to add an image: Screenshot of Google Search Console’s coverage report.
3. Why is my page crawled but not indexed?
Common reasons include technical errors (e.g., server issues, incorrect robots.txt configuration), low-quality or duplicate content, poor website structure, and manual actions from Google.
4. How can I fix the “crawled, not indexed” issue?
Solutions include resolving technical errors, improving content quality, optimizing website structure, and ensuring compliance with Google’s guidelines. Regularly update your content and submit a sitemap to Google.
Where to add an image: Diagram showing the steps to fix “crawled not indexed” issues.
5. How long does it take for a page to be indexed after being crawled?
It varies. Some pages are indexed within a few days, while others may take weeks. Regular updates, high-quality content, and proper website structure can help speed up the process.





Hey people!!!!!
Good mood and good luck to everyone!!!!!
Hey people!!!!!
Good mood and good luck to everyone!!!!!